Create a MacOS app with Intel and Apple Silicon (M1/M2) in Python

Create your .app application for macOS (Intel and M1)
Code changes to create the MyContacts app on macOS Intel and Apple Silicon (M1/M2)
Summary: Step-by-step guide to adapting your PyQt6 project and generating an .app file on macOS, compatible with Intel and Apple Silicon (M1/M2) processors.
Code modifications to create a .app file from the Practical Python book sample application for Mac with x86_64 processors and M-series processors
1.- Create the ResourceManager.py class to obtain the absolute path.
2.- In v_contactos.py you have to remove the assignment of icons to the buttons, lines 59, 65, 71, 77, 83 and 91.
3.- In v_main.py remove the assignment of icons to the buttons, lines 24, 31, 38.
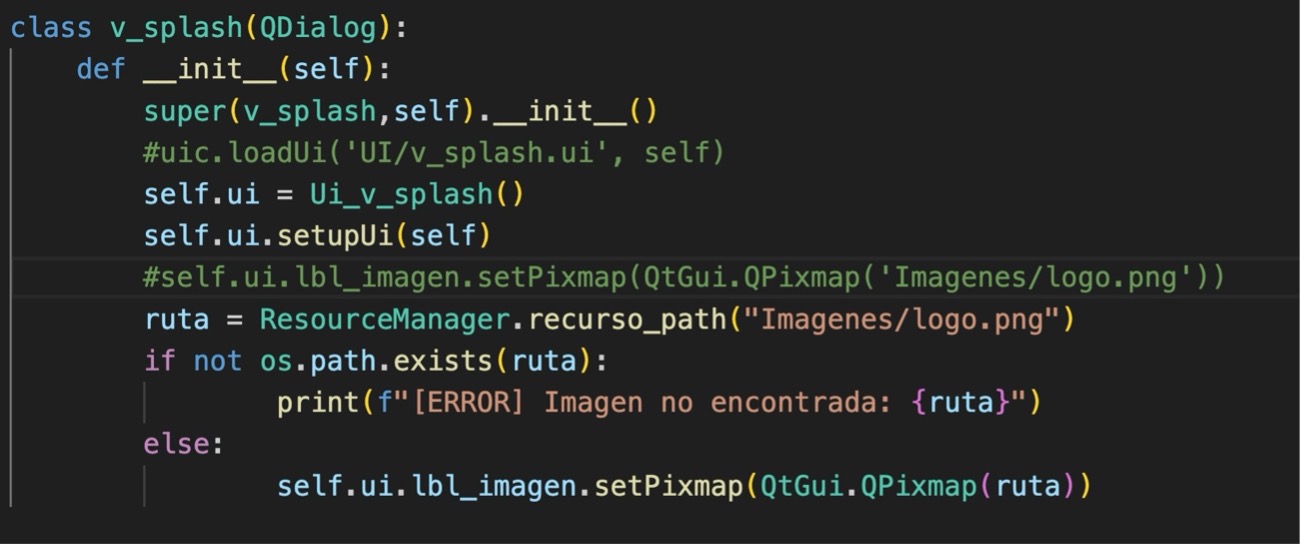
4.- In v_splash.py change the image assignment to:
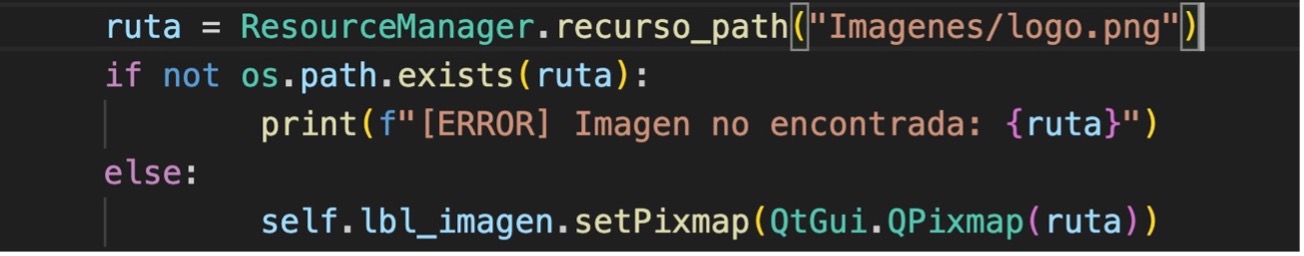
5.- In v_telefonos.py remove the assignment of icons to the buttons, lines 53, 59, 65.
6.- In PantallaContactos.py change the assignment of icons to the buttons for:
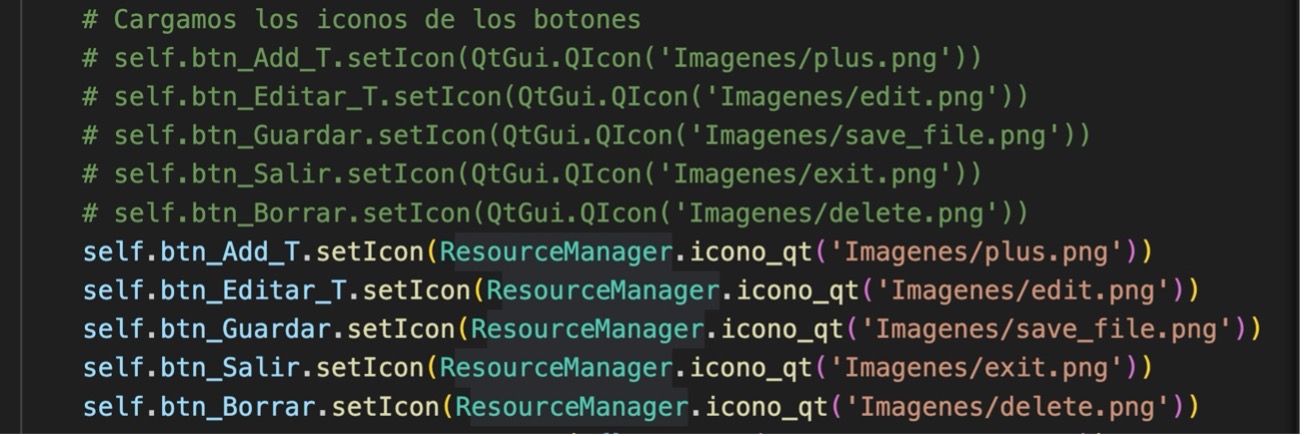
In the toggle_voice_recording and update_text_with_voice methods, the assignment of icons to buttons must be changed using the icon_qt method of the ResourceManager class.
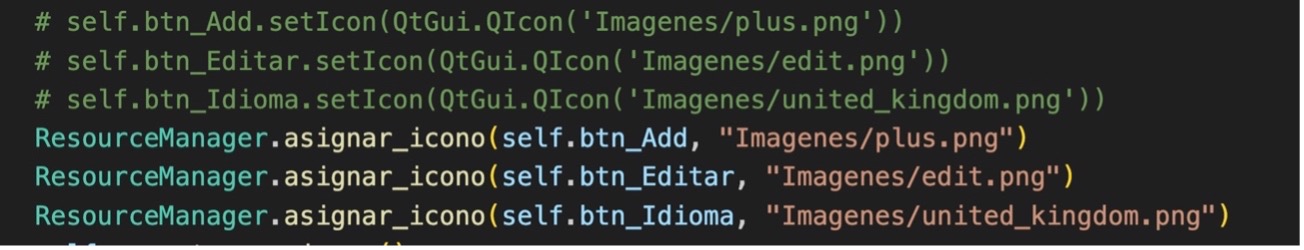
7.- In PantallaMain.py change the assignment of icons to the buttons to:
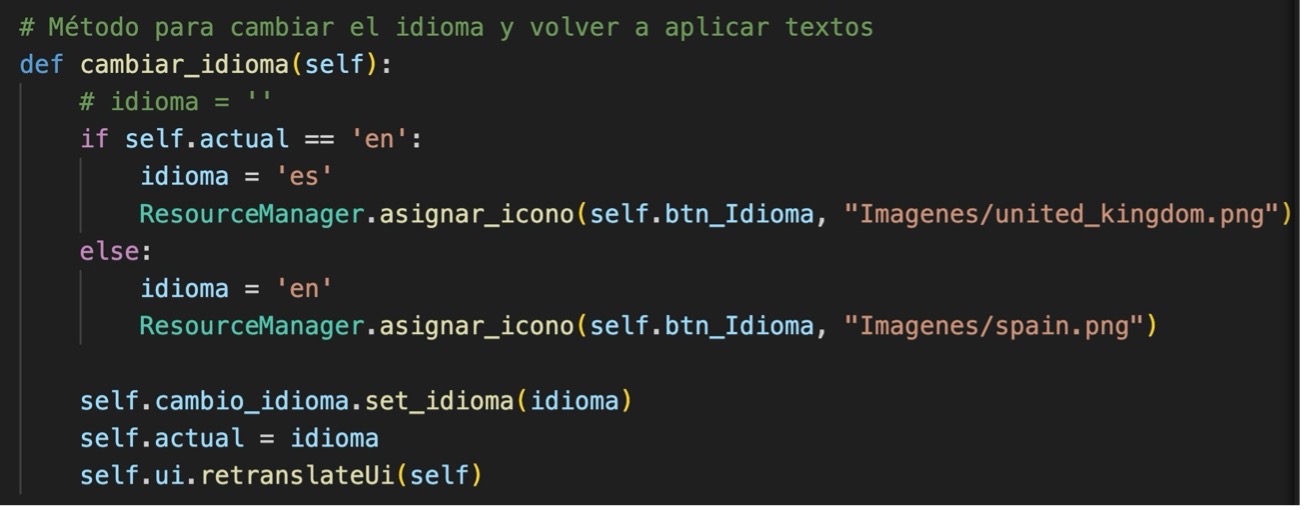
And change the code of the change_language method to:
8.- In PantallaSplash.py modify the image assignment in the __init__ method.
9.- In PantallaTelefonos.py change the assignment of icons to the buttons for:
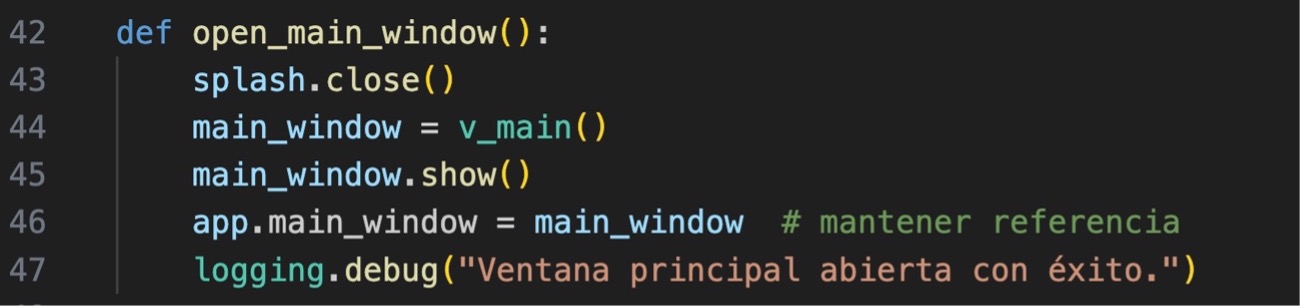
10.- In Principal.py in the open_main_window method, we add line 46 to keep the reference.
11.- In Conexion.py, we need to call the get_db_path method to obtain the correct path for creating the database. We'll modify the __init__ method to change the database connection on line 14 to the get_db_path function call, leaving the code as follows:
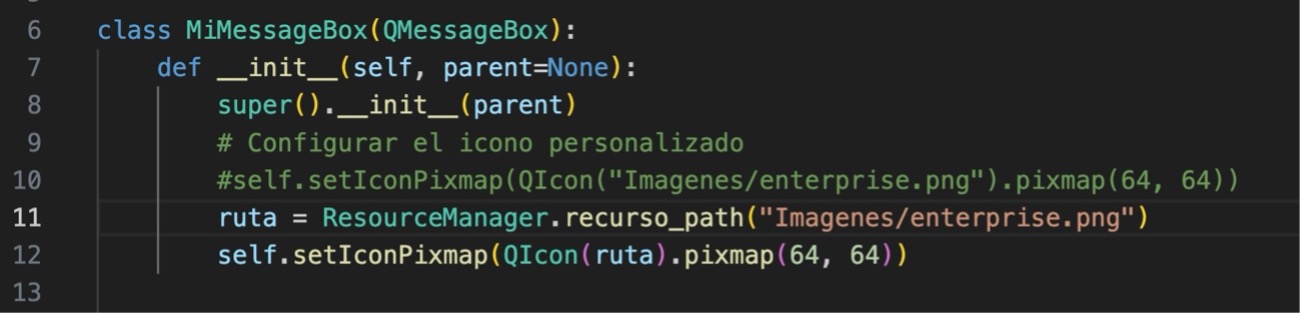
12.- In Messages.py modify the __init__ method of the MiMessageBox class to change the icon assignment as follows:
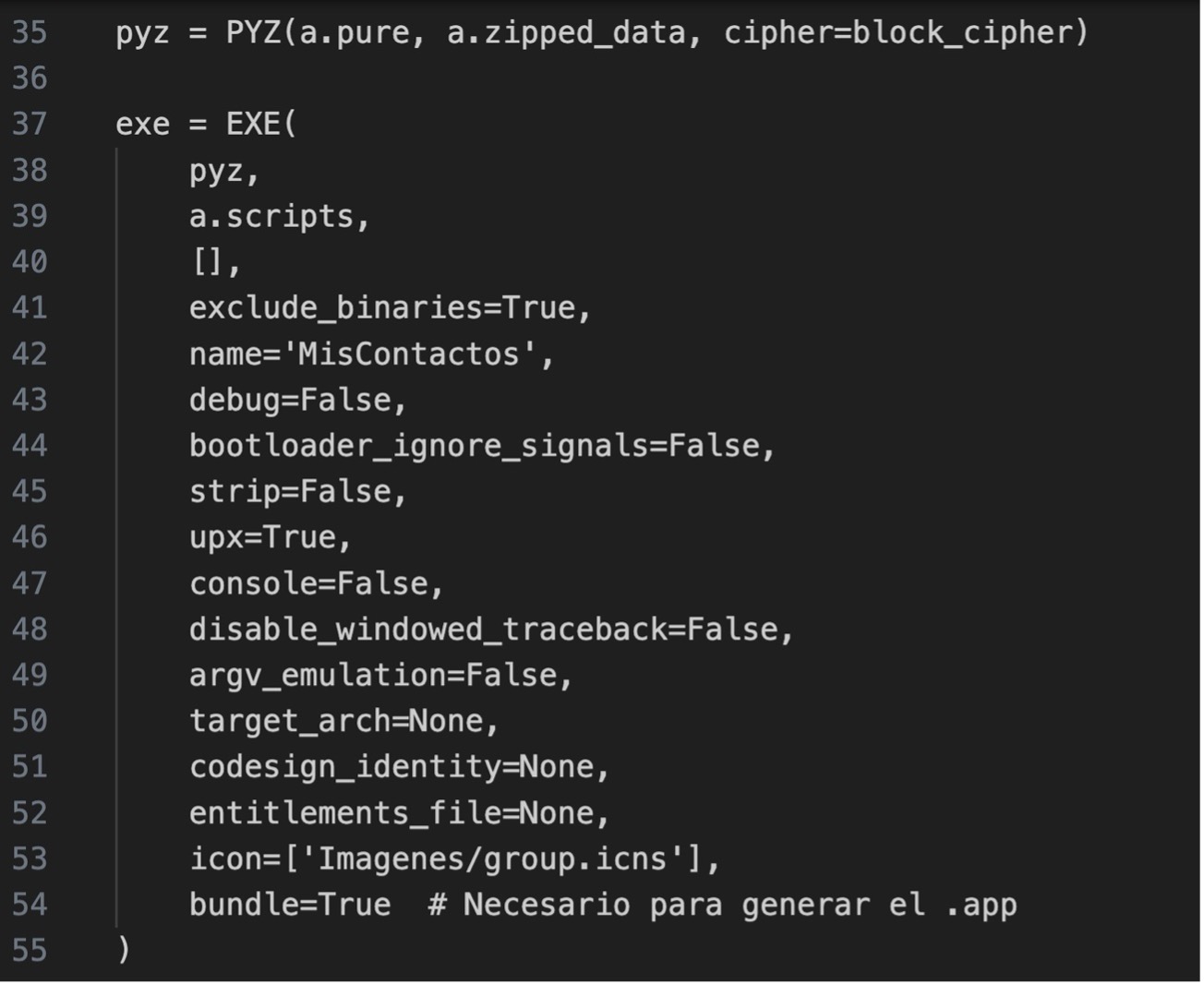
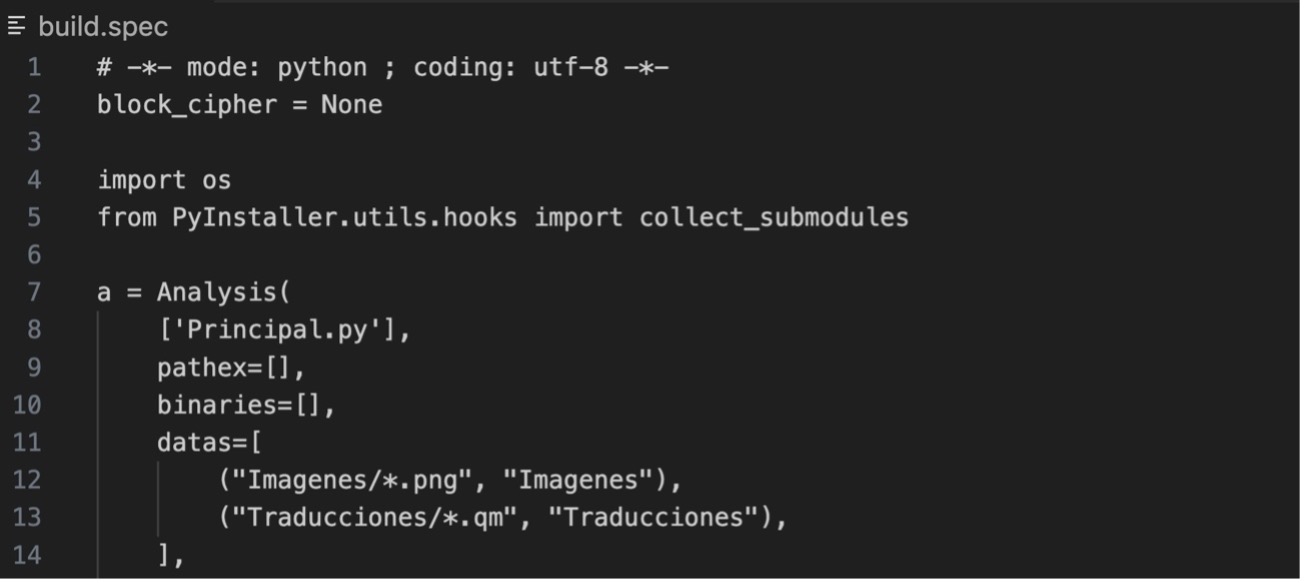
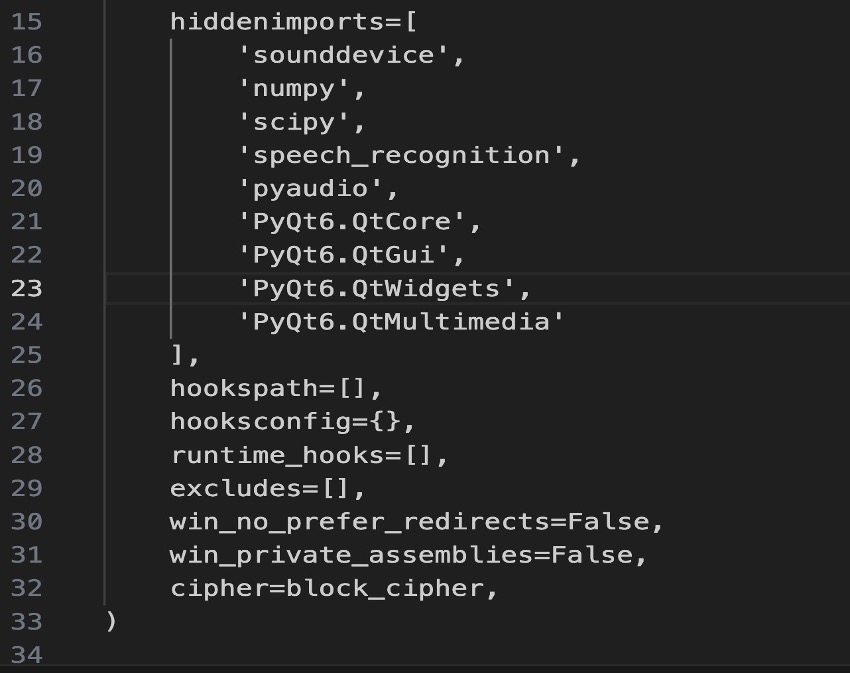
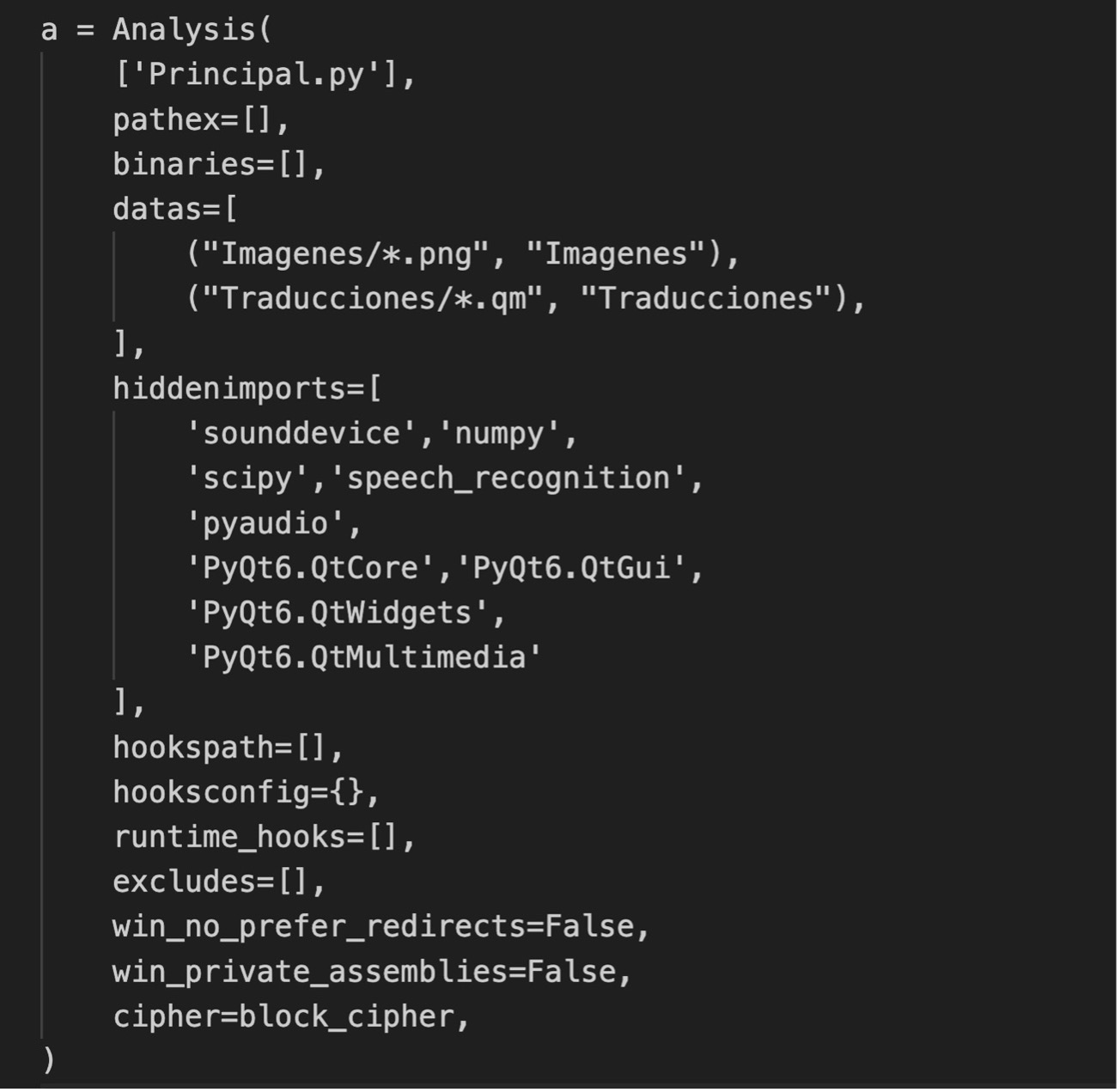
13.- Create build.spec file to generate the .app file with the following code:
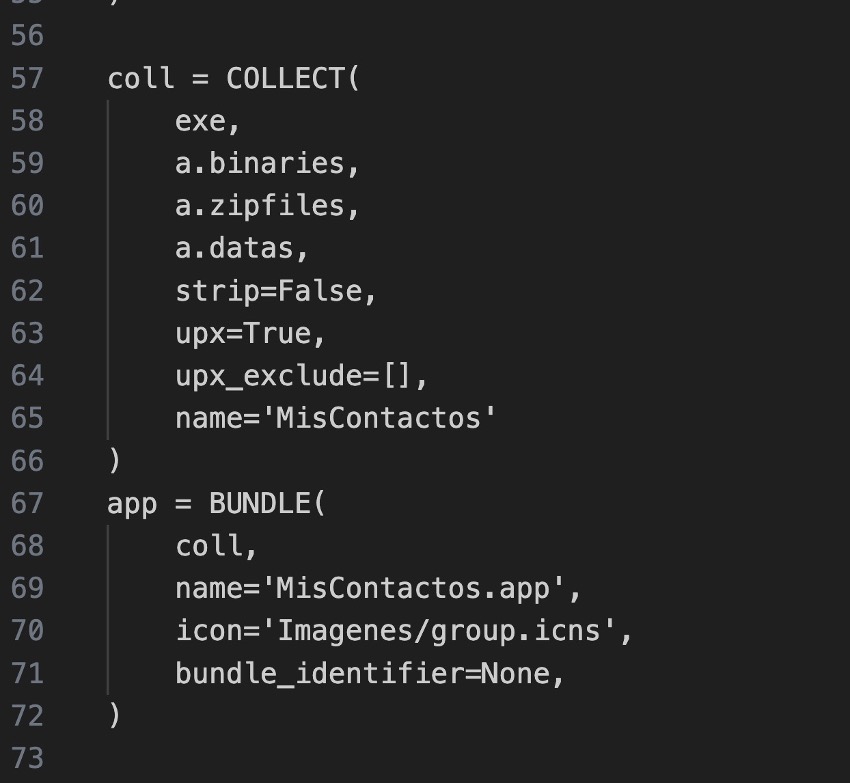


14.- Execute the following command from the terminal:
Este comando creará los directorios build y dist con los archivos necesarios. En dist encontraras el archivo MisContactos.app.
15.- To open the MisContactos.app file, run the following command from the terminal:
If the application crashes when running, we'd need to add a log file to record the steps and be able to detect where the error occurred.
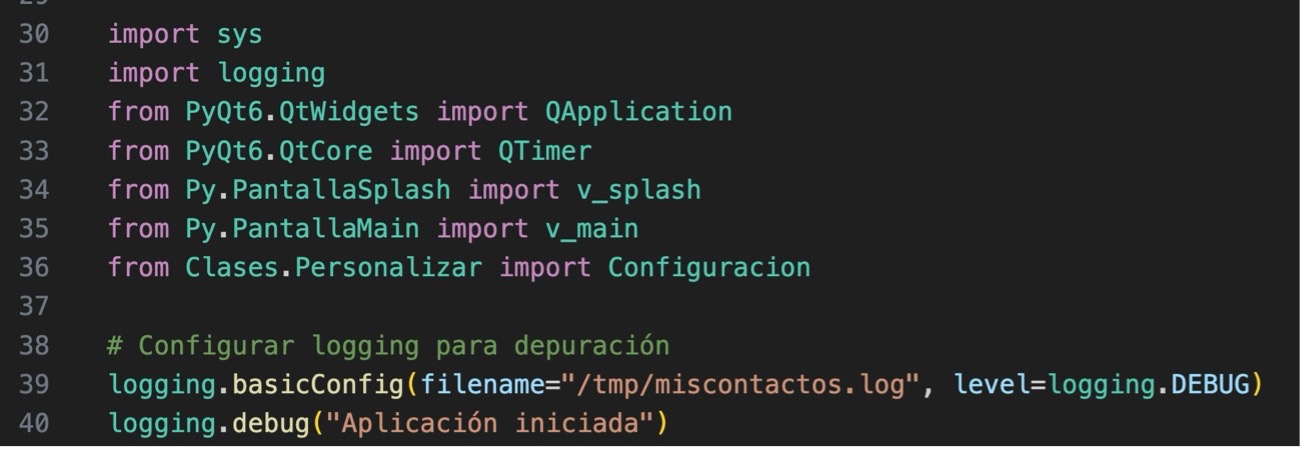
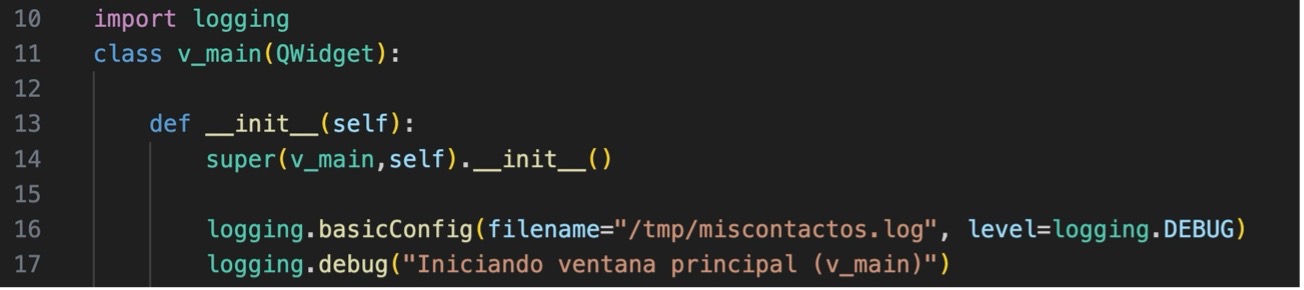
16.- Add code to create a log file. In Principal.py, add lines 39 and 40.
And in the open_main_window method we will add line 47.

In PantallaMain.py we would import logging (line 10) and in the __init__ method we will add lines 16 and 17.
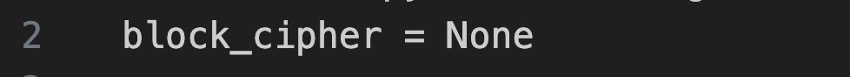
In this way, we will be sending messages to let us know where it has passed correctly and where it has failed.
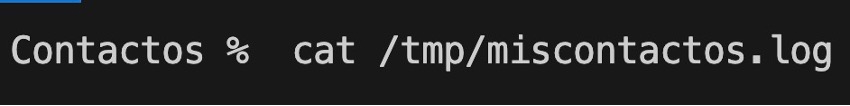
17.- To know the content of the .log file from the terminal we will execute the following command:
Explanation of the .spec file
Explanation of the build.spec file
This indicates that the file is Python and uses UTF-8 encoding.
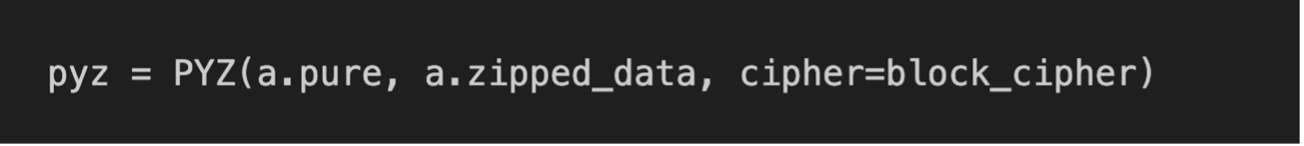
We'll use block_cipher to encrypt files with a key if passwords are used. In our case, it's disabled.
Analysis is the object that analyzes the main script (Principal.py) and detects its dependencies (modules, resources, etc.).
pathex=[] List of additional paths to search for modules.
binaries=[] Additional binary files to include (e.g. DLLs or .dylib on Mac).
datas=[] Data files such as .ui, .png, .db, etc. that the application needs. In our case, we include the images and translations.
hiddenimports=[] To add modules that aren't automatically detected and you need to force their inclusion. In our case, the speech recognition and PyQt6 modules.
hookspath=[] Custom paths for your own hooks. These are Python scripts that tell the tool what to include in the final application, such as data files or hidden import modules, to ensure the application works correctly.
hooksconfig={} Specific configuration for those hooks.
runtime_hooks=[] These are scripts that run just before your application starts. They're used to change paths, environment variables, etc.
excludes=[] Aquí añadiremos los módulos que quieres excluir manualmente del bundle.
win_no_prefer_redirects=False. Disables the Windows operating system's preference for file redirection.
win_private_assemblies=False. Disables the option to include private assemblies when building a Windows executable.
cipher= To use the encryption that we have defined.
A compressed .pyz file is created that includes the pure Python modules.
A compressed .pyz file is created that includes the pure Python modules.
pyz: This is the file generated previously.
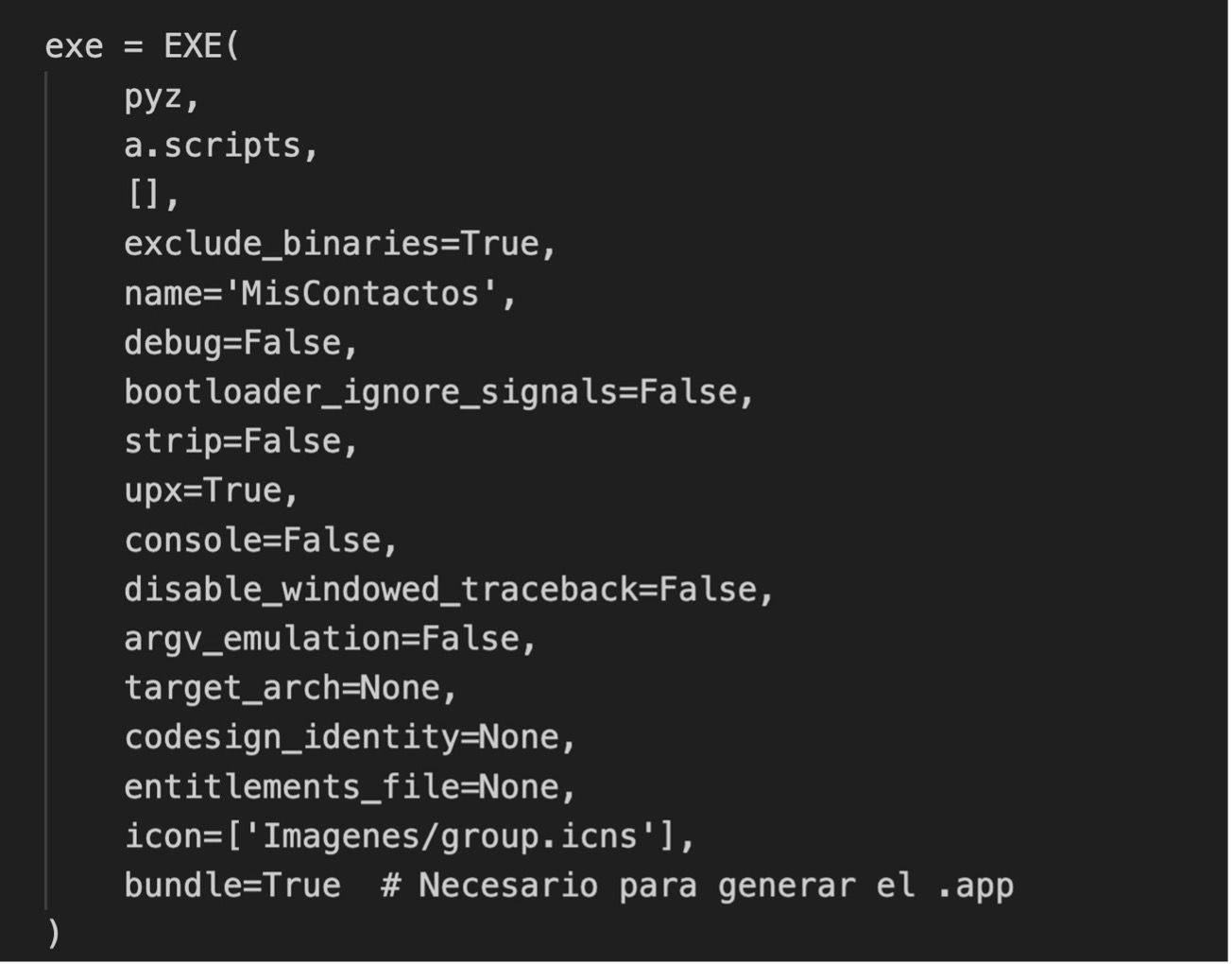
a.scripts: Contains the main script.
exclude_binaries=True: Excludes binaries (moves them to the bundle in COLLECT).
name=’MyContacts’: Name of the final executable.
debug=False: No debugging code is included.
bootloader_ignore_signals=False: If True, ignore system signals.
strip=False: If True, strips debugging symbols.
upx=True: Attempts to compress binaries with UPX (if installed).
console=False: The terminal window is not displayed when running the app.
disable_windowed_traceback=False: Display traceback information in error windows when a Python program terminates due to an unhandled exception.
argv_emulation=False : Disables emulation of sys.arg
target_arch=None. This means that no particular target architecture is specified for the executable to be created.
codesign_identity=None: To sign the app (we leave it empty if it is not signed).
entitlements_file=None: For apps signed with special permissions.
icon=[‘Imagenes/group.icns’]: Icono de la aplicación.
bundle=True: To generate the .app
This step groups all the files into a final application-formatted folder.
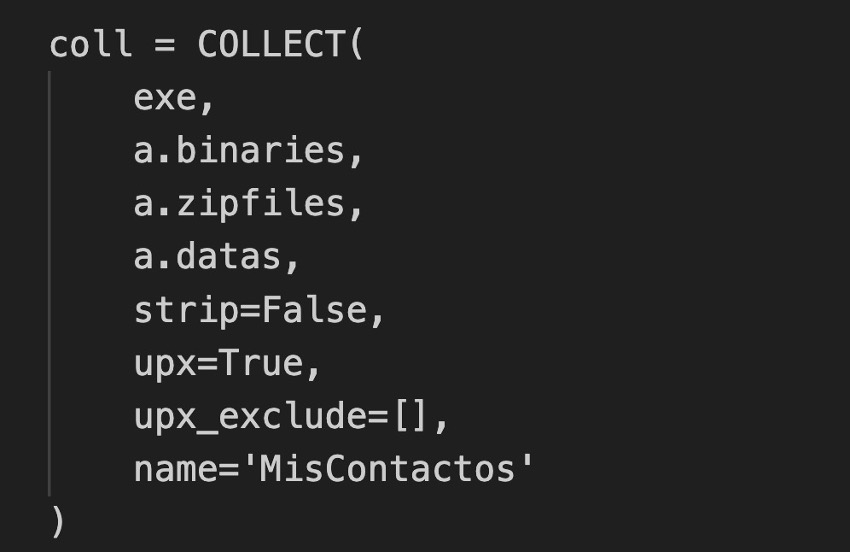
exe: The executable that was created previously.
a.binaries, a.zipfiles, a.datas: Binaries, data, and compressed packages created previously
strip=False: Do not strip debug symbols (usually False in development).
upx=True: Compress if possible.
name=’My Contacts’: Name of the final distribution folder (and the .app).
The .app is defined here:
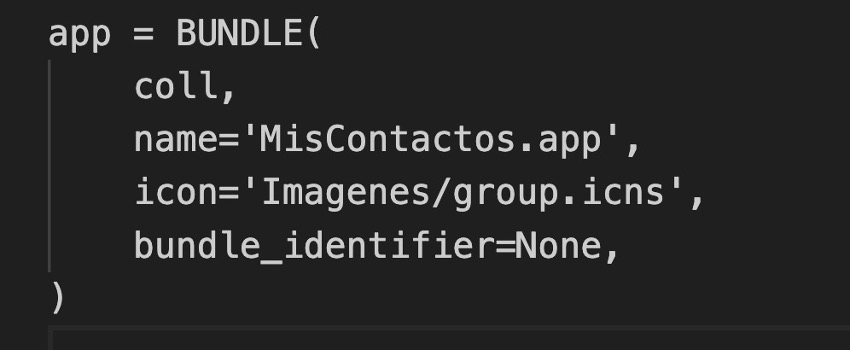
coll: Refers to the grouping of files that we defined previously.
name: Name of the .app file.
icon: Nombre del archivo .icns personalizado.
bundle_identifier: To notarize your app on macOS, usual format: ‘com.company.appname’.
📘 Entry published by Practical Python Team
Do you have questions or want more examples? Visit us at pythonpractico.com

